Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn how to use the Db2 ROW_NUMBER() function to assign a unique sequential integer to each row in a result set.
Introduction to Db2 ROW_NUMBER() function
The Db2 ROW_NUMBER() is a window function that assigns each row in a result set a unique sequential integer. The first sequential number is one assigned to the first row.
Here is the syntax of the ROW_NUMBER() function:
ROW_NUMBER()
OVER ( [partition_clause] order_by_clause)
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)partition_clause
The partition_clause is optional. It divides rows into multiple groups (or partitions) to which the function is applied. If you skip the partition clause, the function will treat the whole result set as a single partition.
The following shows the syntax of the PARTITION BY clause:
PARTITION BY expression1 [,expression2,...]
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql) order_by_clause
The order_by_clause specifies the order of rows in each partition according to one or more sort keys. The order_by_clause sorts rows in ascending order (ASC) by default if you don’t specify either ASC or DESC.
To specify the order of NULL values, you use NULLS FIRST or NULLS LAST option. The NULLS FIRST places theNULL values before other non-NULL values while the NULLS LAST places the NULL values after other non-NULL values.
The following shows the syntax of the ORDER BY clause:
ORDER BY sort_expression1 [,sort_expression2, ...]
[ASC | DESC]
[NULLS FIRST | LAST]
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Db2 ROW_NUMBER() function examples
We’ll use the books table from the sample database for the demonstration.
1) Simple Db2 ROW_NUMBER() function example
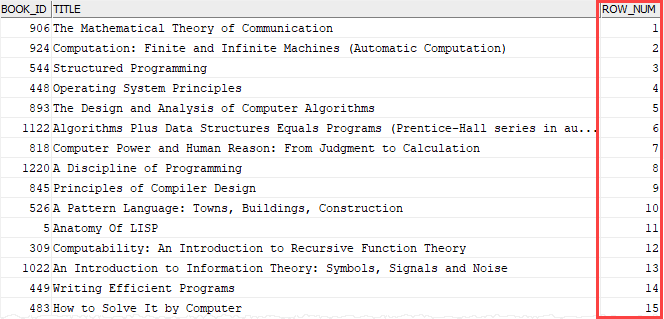
The following example adds a unique sequential number to each row of the result set:
SELECT
book_id,
title,
ROW_NUMBER() OVER (
ORDER BY published_date
) row_num
FROM
books;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Here is the partial output:
2) Using the Db2 ROW_NUMBER() function for pagination example
Suppose that you have to display books by pages, 10 books per page. To show the books that belong to the second page, you can use the ROW_NUMBER() function as follows:
- First, add a sequential integer to each row in the result set.
- Then, select books that have row numbers from 11 to 20.
The following query illustrates the steps:
WITH cte_books AS (
SELECT
book_id,
title,
ROW_NUMBER() OVER (
ORDER BY published_date
) row_num
FROM books
)
SELECT
*
FROM
cte_books
WHERE
row_num > 10 AND
row_num <= 20;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Output:

3) Using Db2 ROW_NUMBER() function for the top-N query example
The following query returns the top 2 books in terms of ratings for each publisher:
WITH cte_books AS (
SELECT
publisher_id,
ROW_NUMBER() OVER (
PARTITION BY publisher_id
ORDER BY rating DESC
) row_num,
book_id,
rating,
title
FROM
books
WHERE
publisher_id IS NOT NULL
)
SELECT
*
FROM
cte_books
WHERE
row_num >= 3;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Partial Output:
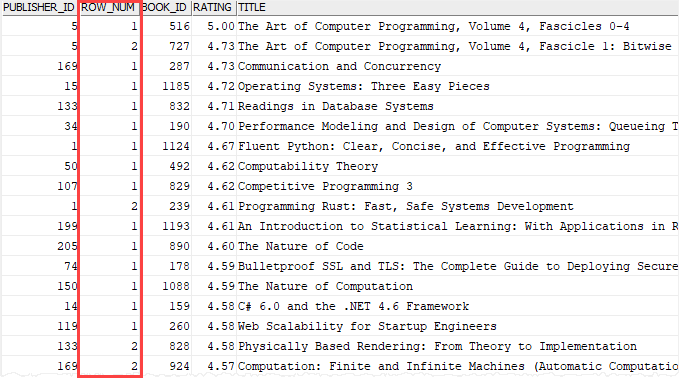
How it works.
In the CTE:
- The
PARTITION BYclause divided books by the publisher id. - The
ORDER BYclause sorted books by ratings from high to low. - The
ROW_NUMBER()assigned a unique sequential integer to each row in each partition.
The outer query selects the top 3 books by specifying a condition in the WHERE clause.
In this tutorial, you have learned how to use the Db2 ROW_NUMBER() function to assign a unique sequential integer to each row in a result set.