Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn how to use the Db2 UNION to combine the result sets of two or more subselects into a single result set.
Db2 UNION Overview
Db2 UNION operator allows you to combine the result sets of two or more subselects into a single result set.
When Db2 encounters a UNION operator, it carries the following operations:
- First, process each subselect to form an interim result table.
- Then, combine these interim tables and delete the duplicate rows to form the final result set.
Here is the syntax of the Db2 UNION:
subselect_1
UNION
subselect_2
</code>Code language: HTML, XML (xml)The queries in the above syntax must meet the following requirements:
- Both subselects must have The number and the order of the columns.
- The data types of the corresponding columns must be the same or compatible via implicit conversion.
The UNION operator is useful to marge lists of values retrieved from multiple tables.
Db2 UNION example
We will use the customers and contacts tables created in the join tutorial for the demonstration.
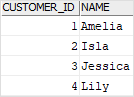
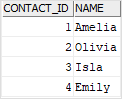
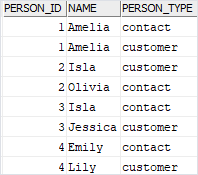
The following query uses the UNION operator to combine the customers and contacts into a single list. To distinguish customers and contacts, we add a new column named person_type.
SELECT
customer_id person_id,
name,
'customer' person_type
FROM
customers
UNION
SELECT
contact_id person_id,
name,
'contact' person_type
FROM
contacts;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Here is the result set:
Using UNION with ORDER BY clause
When you use the ORDER BY clause in a query that uses the UNION operator:
1) You place the ORDER BY clause after the last subselect:
SELECT
select_list
FROM
table_1
UNION
SELECT
select_list
FROM
table_2
ORDER BY
sort_expression;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)2) You can use the column name in the ORDER BY clause if the column in the list has a name. In case the column of a result set does not have a name, you can use the column alias to assign it a name or use a positive integer in the ORDER BY clause to order the rows.
SELECT expression AS name
FROM table_1
UNION
SELECT ...
FROM table_2
ORDER BY name;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)or
SELECT expression
FROM table_1
UNION
SELECT ...
FROM table_2
ORDER BY 1
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)DB2 UNION vs. UNION ALL
The UNION removes all duplicate rows by default. However, if you want to retain the duplicates, you use UNION ALL instead:
subselect_1
UNION ALL
subselect_2
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Db2 UNION ALL example
The following example uses UNION operator that removes all duplicate rows:
SELECT
name
FROM
customers
UNION
SELECT
name
FROM
contacts
ORDER BY
name;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)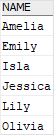
The following picture illustrates the union of two result sets: customers and contacts.
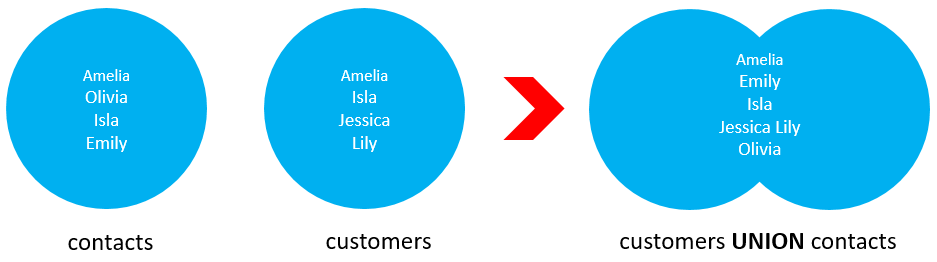
However, the following example uses the UNION ALL operator that retains the duplicate rows:
SELECT
name
FROM
customers
UNION ALL
SELECT
name
FROM
contacts
ORDER BY
name;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)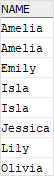
The following picture illustrates the union all of two result sets: customers and contacts.
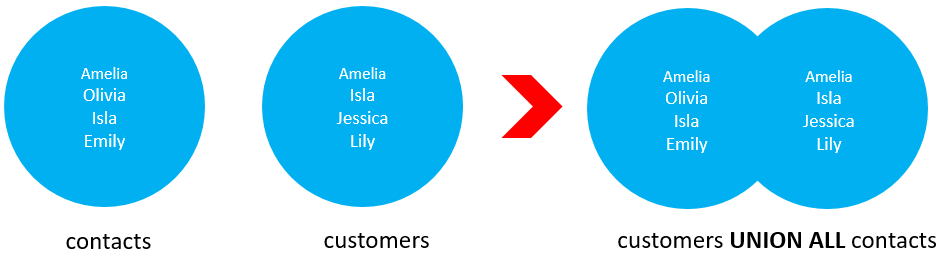
UNION vs. JOIN
The join clause combines columns from two or more tables while the UNION operator combines rows from two or more subselects.
In other words, join appends the result sets from tables horizontally while UNION appends result sets from subselects vertically.
In this tutorial, you have learned how to use the Db2 UNION to combine rows from two or more subselects into a single result set.