Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn how to use the Db2 INNER JOIN clause to query data from two or more related tables.
Introduction to Db2 INNER JOIN clause
The INNER JOIN is one of the join clauses that allow you to query data from two or more related tables. The INNER JOIN clause combines each row from the first table with every row from the second table, keeping only the rows in which the join condition evaluates to true.
The following shows the syntax of joining two tables using the INNER JOIN clause:
SELECT
select_list
FROM
T1
INNER JOIN T2
ON join_condition;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)In this syntax, the join_condition is a Boolean expression that evaluates to true, false, and unknown. Typically, it matches the values of the columns in the table T1 with the values of the columns in the table T2 using the equality operator (=).
The following Venn diagram illustrates the inner join of two tables:
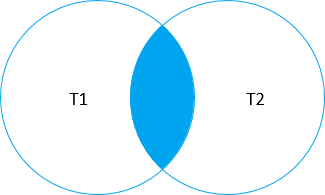
Note that if T1 and T2 tables have the same column names, you must fully qualify these column names in the query e.g., T1.id and T2.id or you will get an error. In case the table names are long, you can use the table aliases to save some typing.
To inner join more than two tables, you use multiple INNER JOIN clauses as shown in the following query:
SELECT
select_list
FROM
T1
INNER JOIN T2 ON join_condition2
INNER JOIN T3 on join_condition3
...;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Db2 INNER JOIN examples
Let’s take some examples of using the INNER JOIN clause.
1) Using DB2 INNER JOIN to join two tables example
The following diagram shows the books and publishers tables:
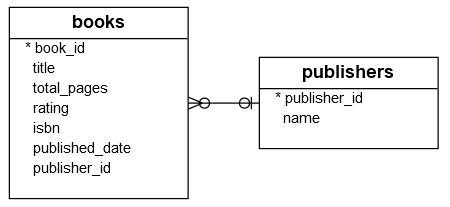
In this model, one publisher may have zero or many books while each book belongs to zero or one publisher. The relationship between the books table and the publishers table is zero-to-many.
The publisher_id column of the books table links to the publisher_id column of the publishers table to establish this relationship.
The following example uses the INNER JOIN clause to join the books table with the publishers table:
SELECT
b.title,
p.name,
b.publisher_id,
p.publisher_id
FROM
books b
INNER JOIN publishers p
ON p.publisher_id = b.publisher_id
ORDER BY
b.title;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Here is the partial output:
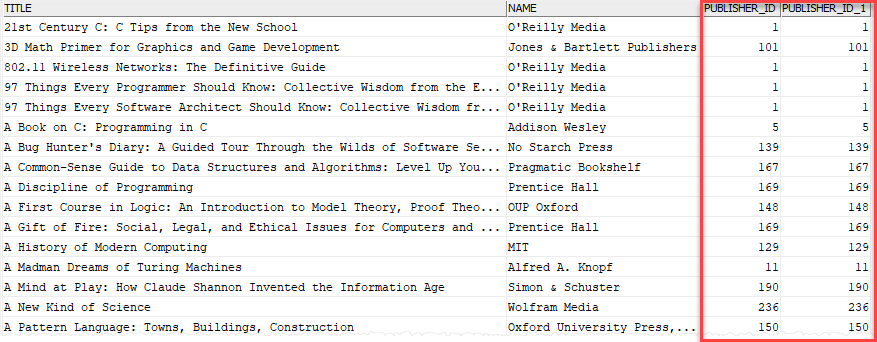
In this example, the INNER JOIN clause compares the value in the publisher_id column of each row in the books table with the value of the publisher_id column of each row in the publishers table. If they are equal, The INNER JOIN combines columns of these two rows into a row and includes this row in the result set.
2) Using DB2 INNER JOIN to join three tables example
See the following books, authors, and book_authors tables:
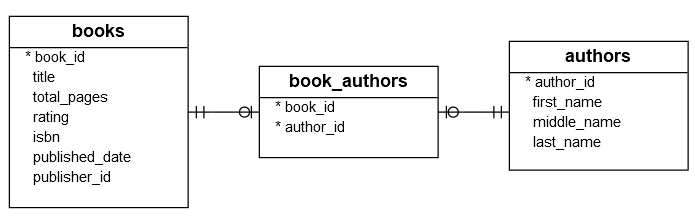
In this model, one book is written by one or many authors. And one author may write one or many books. The relationship between the books table and the authors table is many-to-many.
To model this many-to-many relationship, we have an associated table: book_authors. Note that this associate table is also known as a junction table, a join table, or a cross-reference table.
In order to get the book titles from the books table and author’s names from the authors table, we join three tables using the INNER JOIN clause as follows:
SELECT
b.title,
a.first_name,
a.last_name
FROM
books b
INNER JOIN book_authors ba
ON ba.book_id = b.book_id
INNER JOIN authors a
ON a.author_id = ba.author_id
ORDER BY
b.title;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Here is the partial result set:
In this tutorial, you have learned how to use the Db2 INNER JOIN clause to query data from two or more tables.