Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn about Db2 TIME type and how to use it to store times in the database.
Introduction to Db2 TIME type
The TIME type represents a time of day that consists of three parts: hours, minutes, and seconds. A TIME value ranges from 00.00.00 to 24.00.00.
The following shows the syntax of the time type:
TIME
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Internally, DB2 uses three bytes to store a time value. Each byte consists of two packed decimal digits. The first, second, and third bytes represent the hour, minute, and second respectively.
Db2 stores time values in a special internal format and converts the time values to one of the following formats for the output:
| Format name | Abbreviation | Time format | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| International Standards Organization | ISO | hh.mm.ss | 14.30.10 |
| IBM USA standard | USA | hh:mm AM or PM | 2:30 PM |
| IBM European standard | EUR | hh.mm.ss | 2.30.10 |
| Japanese industrial standard Christian era | JIS | hh:mm:ss | 14:30:10 |
| Installation-defined | LOCAL | Any installation-defined form |
Db2 TIME Literals
Time literals must conform to the following rules:
- Time literals cannot have leading blanks but can have trailing blanks.
- The leading zeros of the hour parts can be skipped, for example,
01:00:00is the same as1:00:00. - The second part of a time literal can be omitted. For example,
01:00:00is the same as01:00. - If the USA format is not used and both minute and second are all zeros, the time literal can be the only hour such as 13 instead of 13:00:00.
If time literals use the USA format, they also conform to the following rules:
- The minute part can be omitted, for example, 1:00 PM is equivalent to 1 PM.
- AM or PM can be in uppercase or lowercase and must be preceded by a single blank.
- The hour must be less than or equal to 12 and cannot be zero except for
00:00 AM
Db2 TIME type example
First, create a new table named daily_routines to store daily routines:
CREATE TABLE daily_routines(
routine_id INT
GENERATED BY DEFAULT AS IDENTITY
NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY,
routine VARCHAR(100) NOT NULL,
start_at TIME NOT NULL
);
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Next, insert five rows into the daily_routines table:
INSERT INTO
daily_routines(routine, start_at)
VALUES
('Get up','06:00'),
('Brush your teeth','06:05'),
('Have breakfast','06:15'),
('Go to school','06:45'),
('Go home','17:00');
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Then, query all data from the table:
SELECT
start_at,
routine
FROM
daily_routines
ORDER BY
start_at;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)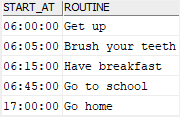
After that, find the routines after 06:05 using the greater than (>) operator:
SELECT
start_at,
routine
FROM
daily_routines
WHERE
start_at > '06:05';
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)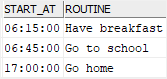
Finally, use the CHAR() function to format times in the USA format:
SELECT
CHAR(start_at, USA) start_time,
routine
FROM
daily_routines
ORDER BY
start_at;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)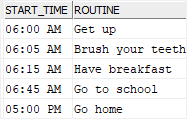
Common Db2 TIME functions
1) Getting the current time
To get the current time of the operating system on which the Db2 instance is running, you use the CURRENT_TIME function:
SELECT
CURRENT_TIME "Current time"
FROM
sysibm.sysdummy1;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Here is the output:
Current time
------------
17:07:28
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Or the following statement also returns the current time. Note that there is a space between the CURRENT and TIME keywords.
SELECT
CURRENT TIME
FROM
sysibm.sysdummy1;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)2) Extracting the hour, minute, and second from a time
To extract time parts such as the hour, minute, and second from a time, you use the HOUR(), MINUTE(), and SECOND() function respectively as shown in the following query:
SELECT
HOUR(CURRENT_TIME) "Current hour",
MINUTE(CURRENT_TIME) "Current time",
SECOND(CURRENT_TIME) "Current second"
FROM
sysibm.sysdummy1;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)The following picture shows the output:
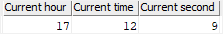
3) Extracting the time from a timestamp
To extract the time part from a timestamp, you use the TIME() function. This statement uses the TIME() function to return the time from the current timestamp:
SELECT
TIME(CURRENT_TIMESTAMP) "Current time"
FROM
sysibm.sysdummy1;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Here is the result:
Current time
------------
17:14:00
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)4) Formatting times
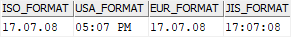
The CHAR() function formats a time in a specified format. For example, the following statement formats a time literal in ISO, USA, EUR, and JIS formats:
SELECT
CHAR(TIME '17:07:08',ISO) ISO_format,
CHAR(TIME '17:07:08',USA) USA_format,
CHAR(TIME '17:07:08',EUR) EUR_format,
CHAR(TIME '17:07:08',JIS) JIS_format
FROM
sysibm.sysdummy1;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Here is the output:
In this tutorial, you have learned how to use the Db2 TIME type and how to store time values in the database.