Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn how to use the Db2 HAVING clause to specify a search condition for groups.
Introduction to Db2 HAVING clause
When you use the SELECT statement to query data from one or more tables, you get a result set that contains all rows of the related tables. To specify a search condition for rows, you use the conditions in the WHERE clause.
Similarly, to specify a search condition for the groups of rows returned by the GROUP BY clause, you use the HAVING clause. The following illustrates the syntax of the HAVING clause:
SELECT
select_list
FROM
table_name
GROUP BY
column1,
column2,
...
HAVING
search_condition;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)The search_condition consists of one or more Boolean expressions that evaluate to true, false, or unknown. The statement returns only groups that satisfy the search_condition. In other words, it returns only groups that cause the search_condition to evaluate to true.
Db2 HAVING clause examples
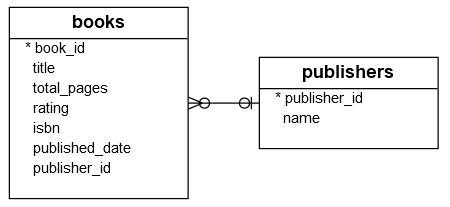
We will use the books and publishers tables from the sample database to demonstrate the HAVING clause.
1) Using Db2 HAVING clause to filter groups example
This statement finds publishers that have more than 30 books:
SELECT
p.name publisher,
COUNT(*) book_count
FROM
books b
INNER JOIN publishers p
ON p.publisher_id = b.publisher_id
GROUP BY
p.name
HAVING
COUNT(*) > 30
ORDER BY
book_count;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)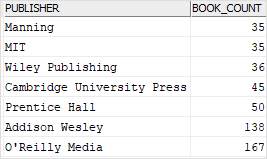
In this example:
- The
GROUP BYandCOUNT(*)function returns publishers with their corresponding book counts - The
HAVINGclause evaluates each group (publisher) and includes only the publishers that have more than 30 books.
2) Using Db2 HAVING clause to find duplicate rows
First, create a new table named t1 for the demonstration.
CREATE TABLE t1
(
id INT NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY,
c1 CHAR(1) NOT NULL
);
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Second, insert some rows into the t1 table.
INSERT INTO t1(id,c1)
VALUES(1,'A'),(2,'B'),(3,'C'),(4,'C'),(5,'A');
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Third, query data from the t1 table.
SELECT
id,
c1
FROM
t1;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)ID C1
----------- --
1 A
2 B
3 C
4 C
5 AAs you can see, the c1 column has some duplicate values e.g., A and C. Finding these duplicate rows in a table with many rows is not easy.
Fortunately, you can use the HAVING clause to find these duplicate values quickly:
- First, group the values in the column from which you want to find duplicates using the
GROUP BYclause. - Second, use the
COUNT()function to get the number of values for each group. - Third, use the
HAVINGclause to filter values whose the number of occurrences is greater than one.
Here is the query:
SELECT
c1,
COUNT(c1) value_count
FROM
t1
GROUP BY
c1
HAVING
COUNT(c1) > 1;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)The following shows the output:
C1 VALUE_COUNT
-- -----------
A 2
C 2In this tutorial, you have learned how to use the Db2 HAVING clause to specify a search condition for groups.