Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn about the Db2 subquery or subselect which is a SELECT statement nested inside another statement such as SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE.
Introduction to Db2 subquery
A subquery is a nested SQL statement that contains a SELECT statement inside the WHERE or HAVING clause of another SQL statement. A subquery is called a subselect.
The subquery allows you to form a search condition based on the data in another table. For example, you can find all books by publishers whose name contains the keyword Oxford:
SELECT
title, rating, publisher_id
FROM
books
WHERE
publisher_id IN (
SELECT
publisher_id
FROM
publishers
WHERE
name LIKE '%Oxford%'
);
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)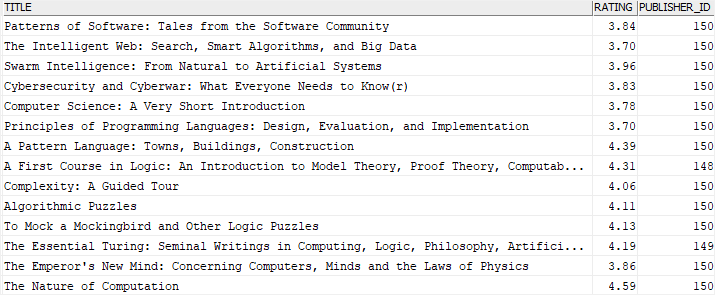
In this example, here is the subquery:
SELECT
publisher_id
FROM
publishers
WHERE
name LIKE '%Oxford%';
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)The subquery is always enclosed in parentheses.
A subquery is also known as an inner query or inner select while the query that contains the subquery is known as an outer query or outer select.
To better understand the result of the outer query, you can imagine that Db2 goes through the following process:
1) DB2 first executes the subquery to get a list of publisher id:
SELECT
publisher_id
FROM
publishers
WHERE
name LIKE '%Oxford%';Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Here is the output:
PUBLISHER_ID
-------------
148
149
150
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)2) DB2 then uses this list for the search condition of the outer query:
SELECT
title,
rating,
publisher_id
FROM
books
WHERE
publisher_id IN (148,149,150);
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)By using the subquery, you are able to combine steps together. The subquery removes the step of selecting the publisher id list and plugging them into the outer select. On top of it, the result of the query is automatically adjusted whenever the publisher data changes.
Nested Subqueries
Db2 allows you to nest a subquery within another subquery. The relationship between the nested subquery and subquery is the same as the relationship between the subquery and outer query. The maximum level of nesting in Db2 is 15.
Db2 Subquery types
Db2 allows you to use a subquery in the following:
- in the place of expression in the
SELECTclause - in the
FROMclause - within the
INorNOT INoperator in theWHEREclause. - within the
ANYorALLoperator in theWHEREclause - within the
EXISTSorNOT EXISTSoperator in theWHEREclause.
1) Using a subquery in place of an expression example
When a subquery returns a single value, you can place it in place of an expression e.g., in the select list of the SELECT clause.
This example uses a subquery to find the average number of pages of all books in the books table:
SELECT
title,
total_pages,
(SELECT
ROUND(AVG(total_pages),0)
FROM
books
) avg_pages
FROM
books
ORDER BY
title;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)
2) Using a subquery with IN operator example
You often use a subquery with the IN operator. In this case, the subquery returns zero or multiple values. The outer query makes use of these values as a filter.
The following statement returns all books from the authors whose first name is Tim.
SELECT
title
FROM
books b
INNER JOIN book_authors A
ON A.book_id = b.book_id
WHERE author_id IN (
SELECT
author_id
FROM
authors
WHERE
first_name = 'Tim'
);
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)
In this example, the subquery returns a list of author ids which are used in the outer query to find their books.
3) Using subquery with ANY operator example
The following illustrates the syntax of a subquery used with the ANY operator:
expression comparison_operator ANY (subquery)
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Suppose, the subquery returns a list of value v1, v2, …. The ANY operator returns true if one of the following comparison pair evaluates to true:
(expression, v1)
(expression, v2)
(expression, ...)
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Note that the comparison operators are =, >, >=, <, <=, and <>.
The following statement uses a query in the ANY operator to find books which have more than five authors.
SELECT
book_id,
title,
rating
FROM
books
WHERE
book_id = ANY(
SELECT
book_id
FROM
book_authors
GROUP BY
book_id
HAVING
COUNT(author_id) > 5
);
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)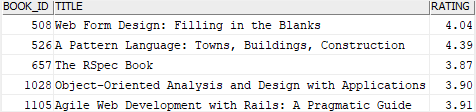
4) Using a subquery with ALL operator example
The syntax of using a subquery with the ALL operator is similar to the syntax of using the subquery with the ANY operator:
expression comparison_operator ALL (subquery)
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)The ALL operator returns true if all comparison pairs return to TRUE.
This statement uses the ALL operator to find the books whose ratings are greater than the average rating of all books by publishers:
SELECT
title,
rating
FROM
books
WHERE
rating > ALL(
SELECT
AVG(rating)
FROM
books
GROUP BY publisher_id
);
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)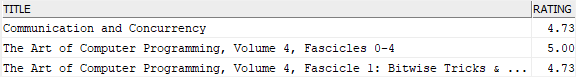
5) Using a subquery with EXISTS operator example
Here is the syntax of using a subquery with EXISTS and NOT EXISTS operator:
WHERE [NOT] EXISTS (subquery)
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)The EXISTS operator returns true only if the subquery returns a non-empty result set. The NOT operator negates the EXISTS operator.
The following query finds the authors who have books published in 2019:
SELECT
first_name,
last_name
FROM
authors a
INNER JOIN book_authors b
ON b.author_id = a.author_id
WHERE
EXISTS (
SELECT
book_id
FROM
books
WHERE
YEAR(published_date) = 2018 AND
book_id = b.book_id
);
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)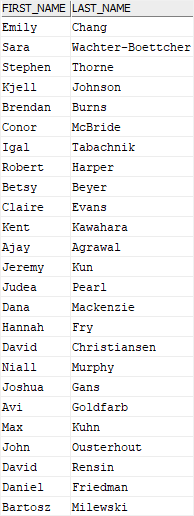
In this tutorial, you have learned about the Db2 subquery and how to use various types of subqueries to query data.