Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn how to use the Db2 GROUP BY clause to group rows into groups.
Introduction to Db2 GROUP BY clause
When you use the SELECT statement to query data, you get a result set which consists of rows. To divide these rows into groups, you use the GROUP BY clause as shown in the following query:
SELECT
select_list
FROM
table_name
GROUP BY
column1, column2,...;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)This statement divides rows derived from the FROM clause into groups by one or more column expression (column1, column2, …) specified in the GROUP BY clause.
When selecting groups of rows from the database, we are interested in the characteristics of the groups, not individual rows. Therefore, we often use aggregate functions in conjunction with the GROUP BY clause.
An aggregate function takes multiple rows as an input and returns a single value for these rows. Some commonly used aggregate functions are AVG(), COUNT(), MIN(), MAX() and SUM(). For example, the COUNT() function returns the number of rows for each group. The AVG() function returns the average value of all values in the group.
Here is the common query that uses the GROUP BY clause with an aggregate function:
SELECT
column1,
column2,
...
aggregate_function(expression)
FROM
table_name
GROUP BY
column1,
column2,
...;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Notice that any column listed in the select list that is not in the aggregate function expression must be placed in the GROUP BY clause, or you will get an error.
Db2 GROUP BY clause examples
Let’s use the books and publishers tables from the sample database for the demonstration.
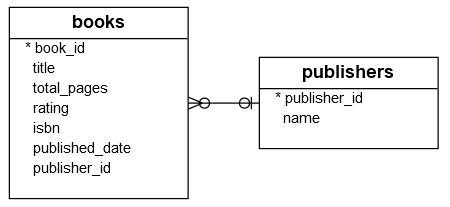
1) Using Db2 GROUP BY clause with COUNT(*) function
This statement uses the GROUP BY clause with the COUNT(*) function to find the number of books by publishers:
SELECT
publisher_id,
COUNT(*) book_count
FROM
books
GROUP BY
publisher_id;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)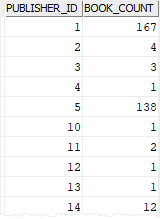
In this statement:
- The
GROUP BYclause divides the rows in the books table into groups by the values in thepublisher_idcolumn. - The
COUNT(*)returns the number of rows per group.
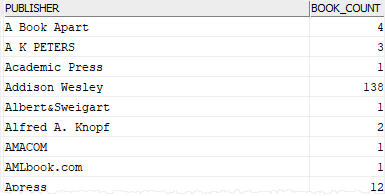
If you want to get the publisher name instead of id, you can join the books table to the publishers table as shown in the following query:
SELECT
p.name publisher,
COUNT(*) book_count
FROM
books b
INNER JOIN publishers p
ON p.publisher_id = b.publisher_id
GROUP BY
p.name
ORDER BY
publisher;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Here is the output:
2) Using Db2 GROUP BY clause with AVG() function
This example uses the GROUP BY clause to find the average rating of all books for each publisher.
SELECT
publishers.name publisher,
DECIMAL(AVG(rating),5,2) avg_rating,
COUNT(*) book_count
FROM
books
INNER JOIN publishers
ON publishers.publisher_id = books.publisher_id
GROUP BY
publishers.name
ORDER BY
publisher;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)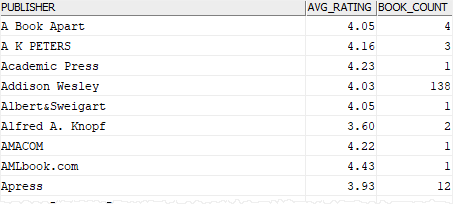
In this example:
- The
GROUP BYclause divides the books into groups by the publisher names. - The
AVG()function returns the average rating of all books for every publisher.
Notice that we keep the COUNT(*) function in the select list to view the number of books for each publisher.
3) Using Db2 GROUP BY clause with MIN() and MAX() functions
The following example finds the minimum & maximum ratings of books for each publisher using the MIN() and MAX() function with the GROUP BY clause:
SELECT
publishers.name publisher,
MIN(rating) min_rating,
MAX(rating) max_rating
FROM
books
INNER JOIN publishers
ON publishers.publisher_id = books.publisher_id
GROUP BY
publishers.name
ORDER BY
publisher;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)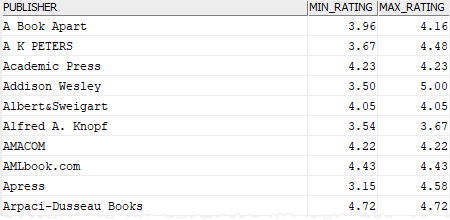
4) Using Db2 GROUP BY clause with SUM() function
This example uses the GROUP BY clause with the SUM() function to find the total pages of all books for each publisher.
SELECT
publishers.name publisher,
SUM(total_pages) total_pages
FROM
books
INNER JOIN publishers
ON publishers.publisher_id = books.publisher_id
GROUP BY
publishers.name;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)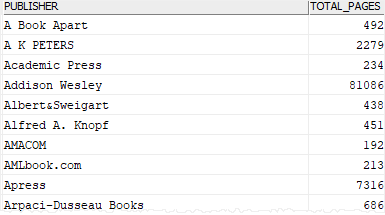
In this tutorial, you have learned how to use the Db2 GROUP BY clause to divide rows into groups by one or more specified columns.